코딩테스트 연습 - 지형 이동
[[1, 4, 8, 10], [5, 5, 5, 5], [10, 10, 10, 10], [10, 10, 10, 20]] 3 15 [[10, 11, 10, 11], [2, 21, 20, 10], [1, 20, 21, 11], [2, 1, 2, 1]] 1 18
programmers.co.kr
그래프 문제가 풀고싶던 와중에 문제 제목만 봐도 그래프 문제 느낌이 나서 오늘은 "지형 이동" 문제를 풀어 보겠습니다.
문제 속에 핵심찾기.
문제를 보면 아무 칸에서 출발하여 모든 칸을 방문할 때 비용의 최솟값을 return하는 문제입니다.
따라서 모든 칸을 최소 비용의 간선으로 잇는 점을 보아 크루스칼 알고리즘을 떠올릴 수 있습니다.
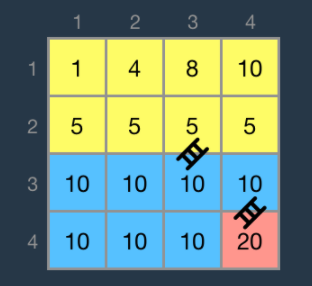
문제의 예시에서 또 하나의 아이디어를 주고 있는것 같습니다.
필자는 색상으로 구역을 나눈 모습을 보고 아이디어를 떠 올렸습니다.
풀이.
1. 서로 이동할 때 사다리 설치가 필요하지 않은 칸들을 하나의 구역으로 구역을 모두 나누어 주겠습니다.
function devideTheLand(land, height) {
const N = land.length;
const devidedLand = Array.from({ length: N }, () => []);
let number = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (!devidedLand[i][j]) {
number += 1;
devidedLand[i][j] = number;
const queue = [[i, j]];
let index = 0;
while (queue.length > index) {
const [y, x] = queue[index++];
for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
const nx = x + dx[k];
const ny = y + dy[k];
if (
nx >= 0 &&
ny >= 0 &&
nx < N &&
ny < N &&
!devidedLand[ny][nx]
) {
if (height >= Math.abs(land[y][x] - land[ny][nx])) {
devidedLand[ny][nx] = number;
queue.push([ny, nx]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
return [devidedLand, number];
}bfs를 통해 구역을 나누어 보면 다음 이미지와 같은 배열을 얻을 수 있습니다.
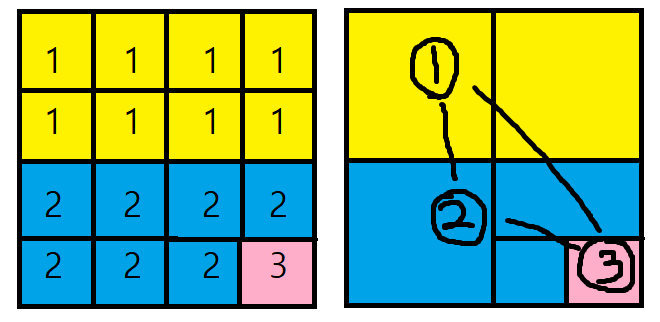
나누어 보니 1, 2, 3번 노드 형식의 심플한 vertex, edge 모습이 나오는 것 같습니다.
2. 서로 다른 구역의 인접한 칸으로 이동할 때 (현재 구역, 다음 구역, 비용)과 같은 edge를 만들어 주겠습니다.
function makeEdges(land, devidedLand) {
const N = land.length;
const edges = [];
const visit = Array.from({ length: N }, () => Array(N).fill(false));
visit[0][0] = true;
const queue = [[0, 0]];
let index = 0;
while (queue.length > index) {
const [y, x] = queue[index++];
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
const nx = x + dx[i];
const ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < N && ny < N) {
const nowLandNum = devidedLand[y][x];
const nextLandNum = devidedLand[ny][nx];
const diff = Math.abs(land[y][x] - land[ny][nx]);
if (nowLandNum !== nextLandNum) {
edges.push([nowLandNum, nextLandNum, diff]);
edges.push([nextLandNum, nowLandNum, diff]);
}
if (!visit[ny][nx]) {
visit[ny][nx] = true;
queue.push([ny, nx]);
}
}
}
}
return edges;
}edges 또한 bfs를 통해 쉽게 만들 수 있는 모습입니다.
이제 크루스칼 알고리즘을 적용하기 전 모든 과정을 끝났습니다.
3. 크루스칼 알고리즘을 통해 모든 구역을 방문할 때 최소 비용을 구해주는 과정에서 정답을 찾아줍니다.
전체 코드.
const dx = [1, 0, -1, 0];
const dy = [0, 1, 0, -1];
// bfs로 구역 나누기.
function devideTheLand(land, height) {
const N = land.length;
const devidedLand = Array.from({ length: N }, () => []);
let number = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (!devidedLand[i][j]) {
number += 1;
devidedLand[i][j] = number;
const queue = [[i, j]];
let index = 0;
while (queue.length > index) {
const [y, x] = queue[index++];
for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
const nx = x + dx[k];
const ny = y + dy[k];
if (
nx >= 0 &&
ny >= 0 &&
nx < N &&
ny < N &&
!devidedLand[ny][nx]
) {
if (height >= Math.abs(land[y][x] - land[ny][nx])) {
devidedLand[ny][nx] = number;
queue.push([ny, nx]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
return [devidedLand, number];
}
// bfs로 서로 다른 구역 이동 간선 만들기
function makeEdges(land, devidedLand) {
const N = land.length;
const edges = [];
const visit = Array.from({ length: N }, () => Array(N).fill(false));
visit[0][0] = true;
const queue = [[0, 0]];
let index = 0;
while (queue.length > index) {
const [y, x] = queue[index++];
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
const nx = x + dx[i];
const ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < N && ny < N) {
const nowLandNum = devidedLand[y][x];
const nextLandNum = devidedLand[ny][nx];
const diff = Math.abs(land[y][x] - land[ny][nx]);
if (nowLandNum !== nextLandNum) {
edges.push([nowLandNum, nextLandNum, diff]);
edges.push([nextLandNum, nowLandNum, diff]);
}
if (!visit[ny][nx]) {
visit[ny][nx] = true;
queue.push([ny, nx]);
}
}
}
}
return edges;
}
function unionFind(n) {
this.parents = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i);
this.getParent = (num) => {
if (num === this.parents[num]) return num;
return (this.parents[num] = this.getParent(this.parents[num]));
};
this.find = (a, b) => {
const aParent = this.getParent(a);
const bParent = this.getParent(b);
return aParent === bParent;
};
this.unionParent = (a, b) => {
const aParent = this.getParent(a);
const bParent = this.getParent(b);
if (aParent > bParent) this.parents[aParent] = bParent;
else this.parents[bParent] = aParent;
};
}
function solution(land, height) {
var answer = 0;
const [devidedLand, landCnt] = devideTheLand(land, height);
const edges = makeEdges(land, devidedLand);
const uf = new unionFind(landCnt + 1);
edges.sort((a, b) => a[2] - b[2]);
let cnt = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
const [from, to, cost] = edges[i];
if (!uf.find(from, to)) {
answer += cost;
uf.unionParent(from, to);
cnt += 1;
}
if (cnt === landCnt - 1) break;
}
return answer;
}
'Nodejs로 알고리즘 박살내기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 19238 스타트 택시 js (0) | 2022.05.03 |
|---|---|
| 백준 3197 백조의 호수 js (0) | 2022.03.20 |
| 백준 4386 별자리 만들기 js (0) | 2022.03.09 |
| 백준 1738 골목길 js (0) | 2022.03.09 |
| 백준 2493 탑 js (0) | 2022.01.15 |